传智播客day16-sql入门
更新日期:
文章目录
SQL入门
Structed Query Language 结构化查询语言
作用: 与数据库进行交互
SQL标准, 由ANSI进行管理和维护. 数据库厂商都支持该标准, 并进行了扩张. 扩张的部分, 一般称之为方言.
常用数据库
- Oracle
- DB2
- MySQL
- SQL Server4
DDL 数据定义语言
数据库操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | -- 创建数据库字符集采用mydb1, 字符集采用默认字符集 create database mydb1; show create database mydb1; -- 显示当前所有数据库 show databases; -- 创建一个字符集为GBK的数据库 create database mydb1 character set gbk; -- 校对规则设置 create database mydb2 character set utf8 collate utf8_general_ci; -- 删除数据库 drop database mydb1; -- 修改数据库 alter database mydb2 character set utf8; |
表操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 | -- 使用mydb1数据库 use mydb1; -- 建表 create table employee( id int, name varchar(200), gender varchar(10), birthday date, entry_date date, job varchar(200), salary float(8,2), resume text ); -- 查看当前数据库中的所有表 show tables; -- 查看表的创建细节 show create table employee; -- 修改表 alter table employee add column image blob; -- 修改列 alter table employee modify job varchar(60); alter table employee drop column image; -- 修改表名 rename table employee to user; -- 修改编码 alter table user character set gbk; alter table user change column name username varchar(100); |
| 数值类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| BIT(1) | 位类型, 默认值为1, 范围 1-64 |
| tinyint[unsigned] | 带符号的范围是-128到127 |
| bool, boolean | 使用0或1表示真假 |
| smallint | 2的16次方 |
| int | 2的32次方 |
| bigint | 2的64次方 |
| float(M,D) | M指示显示长度, d指定小数weis |
| double(M,D) | 表示比float精度更大 |
| char(size) | 固定长度字符串 |
| varchar(size) | 可变长度 |
| blob lognblob | 二进制数据 |
| text(clob) longtext(longclob) | 大文本 |
| time datetime timestamp | 日期类型 |
DML 数据操作语句
作用: 操作的是表中的记录(数据)
关键字: insert update delete
| mysql特点 | |
|---|---|
| 字符串类型 | 使用单引号 'abcd' |
| 日期类型 | 使用单引号 '2101-02-11' |
| 特殊值 | null |
insert
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | insert into user (id, username, gender) values (1, 'zhw', 'male'); -- 如果客户端为 GBK 编码, 会报错, 因为服务器编码和客户端编码不一致 insert into user (id, username, gender) values (1, '海贼王', 'male'); -- 查询mysql的码表 show variables like 'character%'; -- 告知服务器客户端使用的编码, 为临时方法 set character_set_client=gbk -- 告知服务端客户端查看结果集的编码为, 为临时方法 set character_set_results=gbk; |
update
1 2 3 4 | update user set salary=5000, gender='female' where username='zhw'; update user set salary=salary+1000 |
delete和truncate
1 2 3 | delete from user where username='海贼王'; -- 完全清空一个表, 快速, 删除一张表, 重建一张, 属于DDL truncate table user; |
DQL
数据查询语言
select [distinct] *|{column, column...} from table;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 | -- 查询所有 select * from user; -- 投影查询 select username, gender from user; -- 过滤重复的数据 select distinct gender from user; -- 在结果中进行数据计算 select name, salary+10 from user; -- 使用别名 select name as '姓名', salary+10 工资 from user; -- 使用where语句过滤查询 select * from user where username="zhw"; select * from user where salary>5000; select * from user where (salary+10)>4000; -- between select * from user where salary between 4000 and 5000; -- in select * from user where salary in (5000, 6000, 7000); -- like select * from user where username like '李%'; -- and select * from user where age>20 where salary>5000; -- 排序 默认升序 select * from user order by salary ; select * from user order by salary desc; -- 降序 |
数据完整性
数据完整性是为了保证插入到数据中的数据是正确的, 它防止了用户可能的输入错误
分为三类
- 实体完整
- 域完整性
- 参照完整性
实体完整性
规定表的一行在表中是唯一的实体. 实体完整性通过表的主键来实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | -- 声明id是主键,且自动增长 create table t2( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(100) ) character set gbk; create table t3( id int, name varchar(100), primary key(id) ); |
主键分类:
- 逻辑主键, 不代表实际意义, 只是区分不同记录, 比如ID
- 业务主键, 代表着具体的实际意义, 比如身份证, 用户名
域完整性
数据库表的列必须符合某种特定的数据类型或约束
非空约束: not null
唯一约束: unique
1 2 3 4 5 | create table t4 (
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(12) unique not null,
gender varchar(10) not null
)
|
参照完整性(多表)
表间的关系:
- 一对多
- 多对多
- 一对一
一对多
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | create table department( id int primary key, name varchar(100) ); create table employee( id int primary key, name varchar(100), department_id int, constraint department_id_fk foreign key(department_id) references department(id) ); -- 如果删除 department 中的行, 必须先删除employee的外键 |
多对多
需要多建一个联合主键(用至少两个主键同时作为主键)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | create table teacher ( id int primary key ); create table student( id int primary key ); create table teacher_student ( t_id int, s_id int, constraint t_id_fk foreign key(t_id) references teacher(id), constraint s_id_fk foreign key(s_id) references student(id), primary key (t_id, s_id) ) |
一对一
外键+唯一约束
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | create table person ( id int primary key, name varchar(200) ); create table idcard( id int primary key, person_id int unique, constraint p_id_fk foreign key(person_id) references person(id), ) |
主键关联
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | create table person ( id int primary key, name varchar(200) ); create table idcard( id int primary key, constraint i_id_fk foreign key(id) references person(id), ) |
多表DQL
连接查询
基本语法: from 表1 连接类型 表2 [on 连接条件] [where 筛选条件]
约定: 表一为左表, 表二为右表
- 交叉连接: cross join, 返回左表和右表的笛卡尔积
- 内连接: inner join, 返回满足连接条件的记录
- 隐式内连接
- 显式内连接
- 外连接: out join
- 左外连接 left outer join = left join 返回满足连接条件的记录, 同时返回左表中剩余的其他记录
- 右外连接 同上
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | -- 笛卡尔积 select * from customer, orders; select * from customer cross join orders; -- 内连接 -- 隐式 select * from customer c , orders o where c.id=o.customer_id; -- 显示 select * from customer c inner join orders o on c.id=o.customer_id; -- 左外连接 select * from customer c left join order on c.id=o.customer_id; -- 右外连接 select * from customer c right join order on c.id=o.customer_id; |
子查询
子查询也叫嵌套查询, 是指在 select 子句中嵌套查询语句
1 | select * from orders where customer_id=(select * from customer where name="aabbcc");
|
联合查询
联合查询, union关键字
联合查询是合并两条查询语句的查询结果, 去掉其中的重复结果, 并集
1 | select * from orders where price>200 union select * from orders where id=1;
|
报表查询(使用数据库提供的函数库)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | select count(*) from student; select count(*) from student where math>80; select count(*) from student wehre (chinese+math+english)>250; select sum(math) from student; select avg(chinese) from student; select max(chinese), min(math) from student; select product, sum(price) from orders group by product; select product, sum(price) from orders group by product having sum(price) > 100; |
其他函数
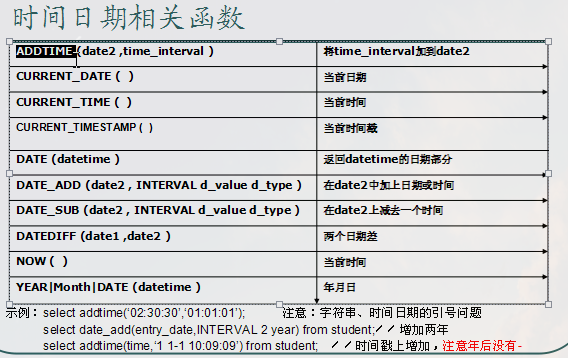
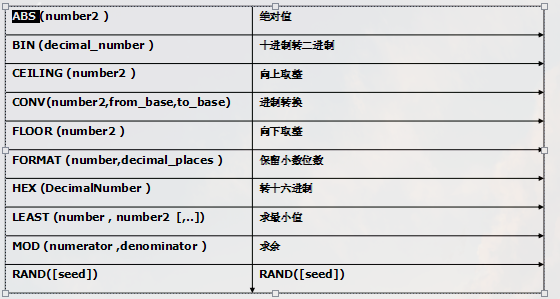
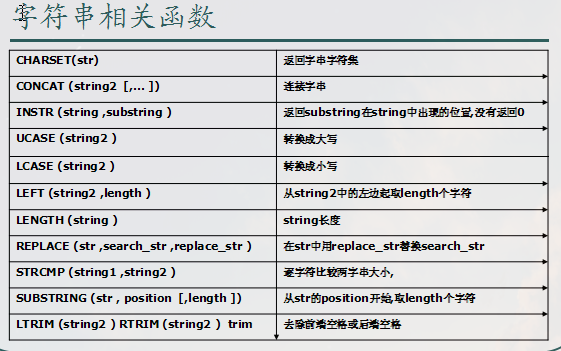
数据库的备份与恢复
1 2 3 4 5 6 | mysqldump -h localhost -u root -p mydb2 > mydb2.sql mysql -uroot -p mydb2 < mydb2.sql # 或 mysql> use db2; mysql> source mydb2.sql; |
