传智播客day22-文件操作和监听器
更新日期:
文件上传
- 必须提供
<input type="file" name=""/>的文件上传输入域 - 表单的提交方式必须是POST方式
- 设置
<form enctype="multipart/form-data">
原理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | <!-- enctype: 指定请求体正文 --> <!-- application/x-www-form-urlencoded(默认) --> <!-- 可选值是multipart/form-data --> <form action="" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input name="text" type="text" /> <input type="file" name="photo"/> </form> |
表单的 enctype 不是 application/x-www-form-urlencoded, 传统的获取方式将失效
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | // enctype = multipart/form-data public void doGet(){ ServletInputStream in = req.getInputStream(); byte b[] = new byte[1024]; int len = -1; while(){ System.ot.println(new String(b, 0, len)); } in.close() } |
运行结果:
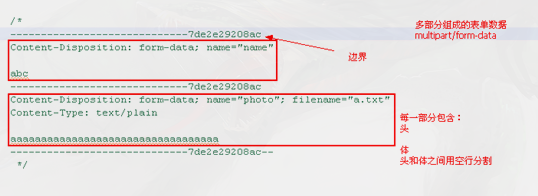
编码
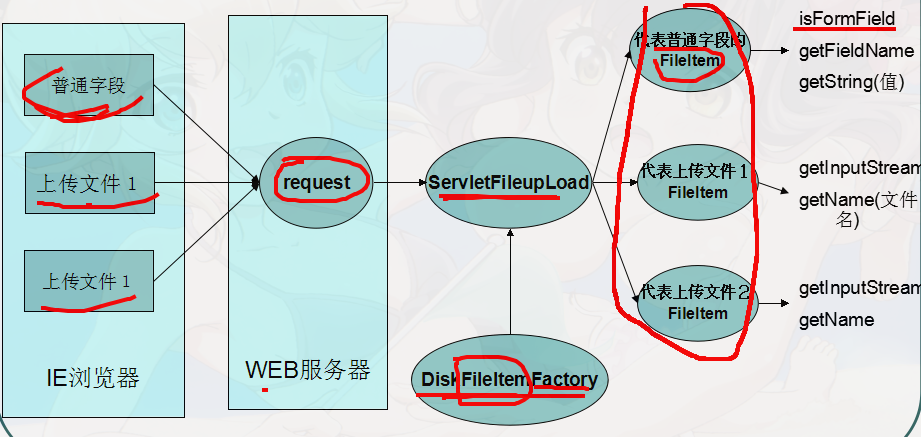
- 搭建环境, 导入
commons-fileupload.jar - 组件的功能是 实现解析
- 上传类的功能解析
DiskFileItemFactory: 产生FileItem对象ServletFileUpload: 解析上传的核心类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 | public void doGet(){ // 验证用户提交的数据是不是mutlipart/form-data类型 boolean isMultiPart = ServletFileUpload.isMultiPartContent(req) // 0. 获取文件上传的真实路径 String storeDir = getServletContext().getRealPath(""); // 1. 创建产生FileItem的工厂实例 DiskFileItemFactory fac = new DiskFileItemFactory(); // 上传过程中要使用缓存, 设置缓存大小, 默认10kb // 如果上传的文件超过10kb, 组建hi采用磁盘临时文件的缓存形式 fac.setSizeThreadhold(int size); // 设置磁盘临时文件的存放目录, 默认是操作系统用户的临时目录 fac.setRepository(File); // 2. 得到解析请求内容的解析器 ServletFileUpload ServletFileUpload sfu = new Servlet(fac); // 3. 解析请求内容, 得到很多的FileItem实例 List<FileItem> items = sfu.parseReqeust(req); // 4. 遍历FileItem的实例 for(FileItem item:items){ if(item.isFormField()){ //4.1 如果是普通字段 String fieldName = item.getFieldName(); // 字段名 // 中文乱码 String fieldValue = item.getString("utf-8"); // 字段值 } else{ //4.2 如果是上传字段 InputStream in = item.getInputStream(); // 获取上传的文件名 String filename = item.getName(); // 根据浏览器不同传的不同, 有的是全路径名, 有的是名字 filename = filename.subString(filename.lastIndexOf("\\") + 1); OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(storeDir + "/" + filename); int len = -1; byte b[] = new byte[1024] while(){ out.write(b, 0, len); } in.close(); out.close(); item.delete(); } } } |
考虑的问题
- 保证服务器的安全
- 把存放文件的目录放在
/WEB-INFO下
- 把存放文件的目录放在
- 中文乱码问题
- 普通字段的中文乱码
FileItem.getString("utf-8")
- 上传的是中文文件名
reqeust.setCharactorEncoding("utf-8")只负责请求体中的
- 普通字段的中文乱码
- 重名文件被覆盖
- 把文件名弄成唯一
filename=UUID.randomUUID.toString()
- 把文件名弄成唯一
防止同一个文件夹下的文件太多
- 分不同的目录存储
- 按照当前的日期存储文件
- 按照UUID文件名的hashCode生成目录
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
String dir = makeDir(storeDir, filename); // 用hashCode计算出一个目录 private String makeDir(String storeDir, String filename) { int hashCode = filename.hashCode(); int dir1 = hashCode&0xf; int dir2 = (hashCode&0xf0) >> 4; String dir = "/" + dir1 + "/" + dir2; File file = new File(dir1, dir2); if(!file.exists()) file.mkdirs(); return dir; }
- 分不同的目录存储
限制文件上传的大小
- 限制单个文件的大小
ServletFileUpload.setFileSizeMax(2*1024*1024)单位是字节,超出时parseReqeust会报错FileUploadBase.FileSizeSizeLimitException
- 限制总文件的大小
ServletFileUpload.setSizeMax(2*1024*1024), 报错FileUploadBase.SizeLimitExceededException
- 限制单个文件的大小
限制上传的文件类型
- 判断文件的扩展名
- 判断文件的MIME类型(Tomcat/conf/web.xml)
1 2
String mimeType = item.getContentType(); if(mimeType.startsWith("image")) todo();
多文件上传时, 有空的表单项
- 通过检查文件MIME也可以避免
- 大文件上传时的临时文件问题
- 组件对于超出缓存的文件会使用临时文件的形式上传, 上传完毕后. 临时文件不会删除,
造成硬盘空间的浪费. 可以通过
FileItem.delete()来配置
- 组件对于超出缓存的文件会使用临时文件的形式上传, 上传完毕后. 临时文件不会删除,
造成硬盘空间的浪费. 可以通过
- 上传进度指示条(目前做不了, 要用到异步交互ajax)
- 注册监听器, 拿到百分比
1 2 3 4 5
ServletFileUpload.setProgressListener( new ProgressListener(){ public void update(long pBytes, long pContentLength, int pItems) { (pBytes + 0.0)/pContentLength; } })
- 注册监听器, 拿到百分比
文件的下载
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | // 罗列可下载的资源 public void doGet(){ //得到 WEB-INF/files 下的文件 String storeDir = getServletContext().getRealPath(); // 递归遍历所有的文件, 把遍历到的信息封装起来 // Map<String,String>.key:UUID, value: 老文件名 Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(); treeWalk(new File(storeDir), map) // 把Map封装到request域中 request.setAttribute("map", map); // 转发到jsp取 request.getRequestDispatcher("/listFiles.jsp").forward(req, res); } public void treeWalk(File file, Map<String, String> map){ if(file.isFile()){ String filename = file.getName(); String oldFileName = filename.subString(filename.indexOf("_") + 1); } else { File[] children = file.listFiles(); for(File f:children){ treeWalk(f, map); } } } |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | <body> <h1></h1> <c:forEach items="" var="me"> <c:url value="/servlet/DownloadServlet" var="url"> <c:param name="filename" value="${me.key}"> </c:param> </c:url> ${me.value} nbsp; <a href="${url}">下载</a> </c:forEach> </body> |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | public void doGet(){
String realFilename= request.getParameter("filename");
realFilename = new String(realFilename.getBytes("ISO8859-1"), "utf-8");
String storeDir = getServletContext().getRealPath();
String dir = makeDir(storeDir, realFilename);
File file = new File(storeDir + dir + "/" + realFilename);
if(file.exists()){
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(file);
// 截取老文件名, 并进行url编码
String oldFileName = realFilename.subString(realFilename.indexOf("_")+1);
oldFileName = URLEncoder.encode(oldFileName, "utf-8");
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename=" + oldFileName);
OutputStream out = response.getOutpuStream();
while(){
out.write(b, 0, len);
}
out.close();
response.getOutpuStream().write("下载成功");// 重写获得outputStream对象
} else {
response.getOutpuStream().write("下载失败".getBytes("utf-8"));
}
}
|
观察者模式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | // 事件源:发生事件的对象 // 监听器: 封装事件的接口 // 事件对象: 封装事件源 Frame f = new Frame("我的窗体"); f.setSize(400, 280); f.setVisible(true); f.addWindowListener(new MyWindowListener()); class MyWindowListener extends WindowAdapter { public void windowsClosing(WindowEvent e){ Frame f = e.getSource(); f.dispose(); } } |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 | // 事件源 public class Student { private String name; private StudentListener listener; public void addStudentListener(){ this.listener = listener; } public Student(String name){} public void study(){ if(this.listener!=null){ listener.preStudy(); } } public void sleep(){ if(this.listener!=null){ listener.preSleep(); } } } // 监听器 public interface StudentListener{ void preStudy(StudentEvent e); void preSleep(StudentEvent e); } // 事件对象 public class StudentEvent{ public StudentEvent(Object source){ this.source = source; } public Object getSource(){ return source; } } |
Servlet 中的监听器
Servlet规范中, 提供了8个监听器(接口)
监听 ServletContext, HttpSession, ServletRequest 三个对象的创建的创建和销毁
- ServletContextListener: 监听 ServletContext 的创建和销毁的监听器
应用启动时执行, 只执行一次
应用场景, 完成系统启动时的初始化工作(Spring框架) - HttpSessionListener: 监听 HttpSession 的创建和销毁的监听器
一个会话对象, 代表着一个客户端, 可以统计网站的访问量 - ServletRequestListener: 监听 ServletReques 的创建和销毁的监听器
可以统计每次页面的访问次数
- ServletContextListener: 监听 ServletContext 的创建和销毁的监听器
监听 ServletContext, HttpSession, ServletRequest 三个对象域中数据变化的监听器
- ServletContextAttributeListener 监听数据的添加删除修改
- HttpSessionAttributeListener 监听数据的添加删除修改
统计登陆用户列表 - ServletRequestAttributeListener 监听数据的添加删除修改
感知型监听器, 这种监听器不需要注册
javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionBindingListener谁实现的这个接口, 就能感知自己合适被 HttpSession 绑定和解绑javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionActiveListener谁实现的这个接口, 就能感知自己合适被 HttpSession 钝化和激活
具体用法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | public class MyServletContextListener extends ServletContextListener{}
<!-- web.xml -->
<listener>
<listener-class>.../MyServletContextListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<listener>
<listener-class>.../MyHttpSessionListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<session-config>
<session-timeout>1</session-timeout> <!-- 一分钟后销毁 -->
</session-config>
|
监听器案例
在线踢人
1 2 3 4 | public class User{ private String username; private String password; } |
Login.jsp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | <body> <form action="loginservlet" method="posj"> <input type="text" name="username"/> <input type="password" name="password"/> <input type="submit"/> </form> </body> |
LoginServlet.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | public void doGet(){
req.setCharactorEncoding("utf-8");
String user = req.getParameter("username");
String password = req.getParameter("password");
User user = new User();
user.setUsername(username);
user.setPassword(password);
request.getSessioin().setAttribute("user", user);
res.sendRedirect(req.getContexPath()); // 重定向到主页
}
|
监听域中数据的变化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | public class OnlineUserListener implement HttpSessionAttributeListener { // 设置登陆标记 // 监听到的目的: 找一个容器 Map<用户名, httpSession> 存起来, 让index.jsp能访问到 // 向任何HttpSession域中放东西, 都会经过该方法 public void attributeAdded(HttpSessionBindingListener e) { HttpSession session = se.getSession(); Object obj = session.getAttribute("user"); if(obj==null){ // 放的标记不是User return; } if(!(obj instanceof User){ return; } ServletContext sc = session.getServletContext(); //存放登陆用户名和对应HttpSession对象 Map<String, HttpSession> map = sc.getAttribute("map"); if(map==null){ map = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<String, HttpSession>());// 线程安全的Map sc.setAttribute("map", map); } map.put((User)obj.getUsername(), session); } } |
index.jsp, 显示当前用户登录的登陆名
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | <body> <c:forEach items="applicationScope.map" var="me"> <c:url value="KickServlet" name="url"> <param name="username" value="${me.key}"> </param> </c:url> ${me.key} <a href="${url}">踢出</a><br/> </c:forEach> </body> |
KickServlet.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | public void doGet(){ String username = request.getParameter("username"); username = new String(username.getBytes("ISO-8859-1", "utf-8")) ServletContext sc = getServletContext(); Map<String, HttpSession> = sc.getParameter("map"); map.get(username).invalidate(); map.remove(username); res.sendRedirect(rq.getContexPath()); } |
国际化
程序提供适合来访者阅读习惯的文本, i18n
固定文本的国际化
固定文本写在一个资源包中, 一个资源包可以包括多个 *.properties的文件
资源的写法
文件基名语言国家.properties 语言 国家有一定的编码, ISO来指定(基名一样)
msg_zh_CN.properties 中国大陆
msg_en_US.properties 美利坚
msg_en_UK.properties 大不列颠
编码案例
msg_en_UK.properties msg_zh_CN.properties
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | // 获取来访者使用的系统的区域位置 ResourceBundle.getBundle("cn.itcast.resources.msg") rb.getString("hello") // 读取美国的 Locale l = Locale.US; ResourceBundle.getBundle("cn.itcast.resources.msg", l) |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | <% Locate l = req.getLocale(); ResourceBundle rb = ResourceBundle.getBundle("", l) %> <form action=""> 用户名: <input/> <%= rb.getString("username")%> </form> <!-- 等价于 --> <fmt:setLocal value="pageContext.request.locale"> </fmt:setLocal> <fmt:setBundle basename="cn.itcast.resources.msg" var="msg"> </fmt:setBundle> <fmt:message key="username" bundle="${msg}"> </fmt:message> |
时间和日期的格式化
DateFormat: 用户所有界面的输入都是String, JavaBean: java.util.date
Date parse(String s): 解析字符串成为日期对象
String format(Date d): 把日期对象转换为字符串
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | Date d = new Date(); DateFormat df = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(); df.format(d); String s = "2014-4-29 12:21:11" Date d = df.parse(s); Locale l = Locale.CHINA; Date d = new Date(); DateFormat df = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormate.Full, DateFormat.Full, l); df.format(d); |
在JSP中
1 2 | <fmt:formateDate value="${now}" type="both|date|time"> </fmt:formateDate> |
数字的格式化, 货币符号
NumberFormat: 用户输入的String, JavaBean:Number
Number parse(String s): 解析
String (Number s): 格式化
1 2 3 4 | Locale l = Locale.CHINA int money = 10000; NumberFormat nf = NumberFormat.getCurrencyFomatter(); nf.format(money) |
批量国际化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | // String pattern = "At 12:30 pm on jul 3,1998, a hurricance destroyed 99 house and caused $100000 of damage" String pattern = "At {0, time, media} on {1, date, medium} a hurricance destroyed {2} house and caused {3, number, currency} of damage"; Date time = new Date(); //数据库发生的日期 Date date = new Date(); // 日期 int num = 99; int money = 100000; MessageFormat mf = new MessageFormat(pattern); String s = mf.format(new Object[]{time, date, num, money}) |
